Antigen-Specific T Cells for Melanoma Research: MART-1
Our scientists were among the first to develop custom antigen-specific T cells for research use and have created them against a diverse range of targets, including viral, tumor, and self-antigens.
We’re now developing the next generation of antigen-specific T cells to target some of today’s most prevalent and challenging diseases. More on that below. But first, a primer on antigen-specific T cells.
The Role of Antigen-Specific T Cells in Disease Research and Treatment
T cells are a major player in the immune response in various diseases, including cancer and pathogenic infections, and are mediators in inflammation and autoimmunity. A large body of research has been conducted over the past few decades to manipulate T cell responses, leading to many clinical strategies including cancer vaccines, T cell adoptive therapy, CAR-T therapy, immune-oncology, and the use of regulatory T cells for autoimmune diseases.
Antigen-specific T cells are an important tool in T cell biology research and potency assays. Investigators can isolate them directly from the disease site (e.g., tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL) or inflammatory lesion infiltrate populations), but these procedures often yield a limited number of cells due to low cell frequency and lack of robust isolation methods.
Alternatively, antigen-specific T cells can be generated in vitro using antigen-presenting cells pulsed with whole antigens or peptides. However, this process is often time-consuming with a low success rate.
About Ignyte Bio’s Antigen-Specific T Cells
Ignyte Bio offers antigen-specific T cells for research use you can rely on.
- Typically generated using multiple in vitro stimulations with peptide antigens
- Not immortalized or genetically modified, so they more closely mimic physiological T cells
- Specificity analyzed using the cognate peptide/MHC tetramer binding as well as interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) secretion assays.
Announcing Ignyte Bio’s Newest Antigen-Specific T Cell Line for Melanoma Research
Melanoma is one of the malignancies that have been studied intensively, particularly in terms of the immune response to tumors, and has been used as a model for the development of immunotherapy.
Read more about our MART-1 specific CD8+ T cells available for purchase.
About the MART-1 Antigen
MART-1 (Melanoma Antigen Recognized by T cells) was coined by Kawakami et. al., 1994 when they identified a shared human melanoma antigen recognized by TILs from metastatic melanoma patients. This protein, also known as Melan-A, is expressed in lower levels in normal melanocyte lineage cells from the skin and retina. Several MART-1-derived peptides have been identified as targets of cytotoxic T cells in melanoma patients. One of the immunodominant peptides — wild-type MART-126-35 (EAAGIGILTV) and its analog, which contains an alanine to leucine substitution at position 27, MART-126-35, 27L (ELAGIGILTV) — have been used in several melanoma vaccine trials. The latter is shown to be more immunogenic resulting from increased binding to the HLA-A-02:01 molecule.
Ignyte Bio’s anti-MART-1-specific CD8+ T cells are generated against the analog peptide MART-126-35, 27L.
Figure 1 shows specific recognition of the MART-126-35, 27L in association with HLA-A-02:01 as shown by the tetramer binding study. Figure 2 shows specific IFN-γ secretion and specific lysis when HLA-A-02:01+ target cells were incubated with both the analog MART-126-35, 27L as well as the wild-type MART-126-35 peptides.
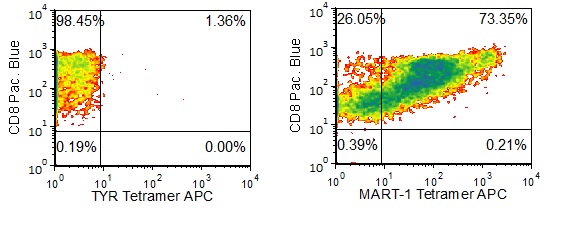
Figure 1. Recognition of Antigenic Peptide (MART-1 26-35, 27L) Demonstrated by Peptide/MHC Tetramer Binding Analysis. Cryopreserved T cells were thawed and stained with APC-labelled HLA-A-02:01-MART-126-35, 27L(ELAGIGILTV, MART-1 Tetramer or a control tetramer HLA-A-02:01-Tyrosinase369-377, 371D (YMDGTMSQV, TYR Tetramer APC. These cells were counterstained with anti-CD8 Pacific Blue reagent and analyzed by flow cytometry. Non-viable cells were excluded from the analysis using 7-AAD.
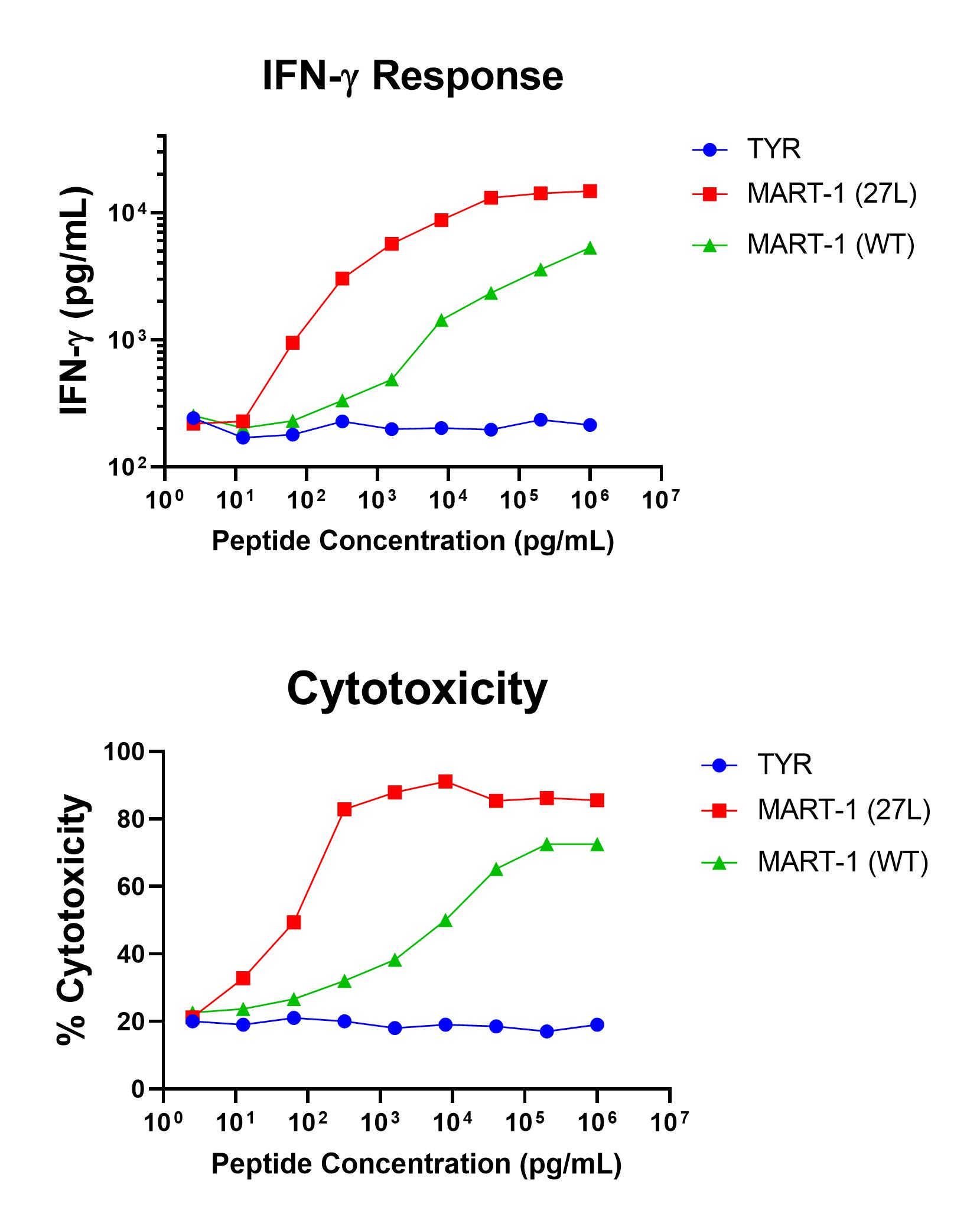
Figure 2. Antigen-Specific IFN-γ Secretion and Cytotoxicity Data. Freshly thawed anti-MART-1 CD8+ T cells were plated at 2 x 104 cells/well in the presence of 2 x 104 T2 cells, an HLA-A-02:01+ B-LCL (ATCC, Manassas, VA) and different concentrations of MART-126-35, 27L (ELAGIGILTV): MART-1 (27L) , MART-126-35 (EAAGIGILTV): MART-1 (WT), or the control peptide Tyrosinase369-377, 371D (YMDGQMSQV): TYR in a 96-well round bottom plate. After 18-24 hours of incubation at 37oC, 5% CO2, culture supernatants were harvested and assayed for IFN-γ using the Lumit™ IFN-γ Immunoassay (Promega, Madison, WI). IFN-γ concentration is plotted against gp100 and control peptide concentrations (upper graph). Remaining cells in each well were stained with the viability dye 7-AAD and analyzed using flow cytometry. % Cytotoxicity (= % 7-AAD+ target cells) is plotted against the respective peptide concentrations (lower graph).
